In this post I will go through a simple example of how to authenticate an .Net Core Controller with Api Key in ASP.NET Core 2.2 API with C#. I am using Visual Studio 2017 with .Net Core 2.2 for developing the API, and postman tool for testing the API.
First create a new project from Visual Studio 2017(you can also use Visual Studio Code with .Net Core CLI to create sample project structure) with project template
ASP.Net Core Web Application .
In the next dialog, it will ask you for the default template to auto-generate required project structure for you, here select the API from given templates.
It will auto-generate a controller ValuesController with different REST action methods.
- Get
- Post
- Put
- Delete
Run the project, and from postman make a call to the values controller's get method (you may have a different port number):
https://localhost:44365/api/values
You will see the output:
Till now, we have created a fresh API project and run it successfully. Lets add Key Authentication in this API.
We will implement a Filter ApiKeyAuthAttribute to check for Api Key in the request header(you may check other sources like querystring, or request body etc).
ApiKeyAuthAttribute will implement the interface IAsyncActionFilter so that it can inspect incoming request for Api Key.
Also it will inherit from Attribute class so that we can use this
filter as an attribute on our controller or action methods where we need authentication.
In ApiKeyAuthAttribute, we have to implement IAsyncActionFilter's member OnActionExecutionAsync
where we will write our logic to check for Api Key.
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Method)]
public class ApiKeyAuthAttribute : Attribute, IAsyncActionFilter
{
private const string ApiKeyHeaderName = "X-Api-Key"; // header-name constant
private const string SecretApiKey = "My Secret"; // store this key in config file or database etc.
public async Task OnActionExecutionAsync(ActionExecutingContext context, ActionExecutionDelegate next)
{
//if no header found, return UnauthorizedResult
if (!context.HttpContext.Request.Headers.TryGetValue(ApiKeyHeaderName, out var requestApiKey))
{
context.Result = new UnauthorizedResult();
return;
}
//if header is found, but key is not maching with our secret key, return UnauthorizedResult
//checking against hardcoded local variable, you may want to store this in external source or call an external service to authenticate provided key.
if (!SecretApiKey.Equals(requestApiKey))
{
context.Result = new UnauthorizedResult();
return;
}
//if reaches here, it means the request has valid apikey, so it is authenticated, call the next middleware component.
await next();
}
}
Next we have to decorate the desired controller(in our case ValuesController) with the custom attribute ApiKeyAuth.
We are done here. Note that we don't have to make any changes in Startup.cs class when you are using Filter as opposed to our last example of
BasicAuthenticationHandler where we need to call AddAuthentication() method on IServiceCollection object to configure the target authentication handler.
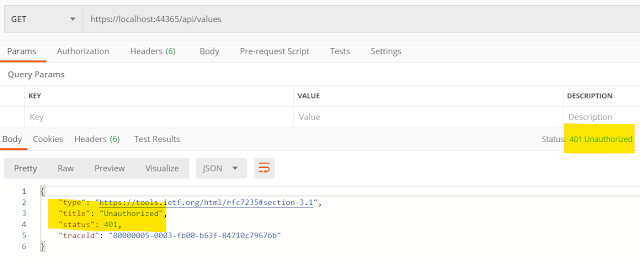
Your API is ready with Key Authentication. With postman if you make a call without X-Api-Key header(or with invalid header value), it will give you 401 error.
With a valid value of X-Api-Key, in our case My Key 123, postman will receive success response.





No comments:
Post a Comment